

As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. For lower elements, the difference between the energy levels of different orbitals is larger and exceptions are not commonly observed. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.
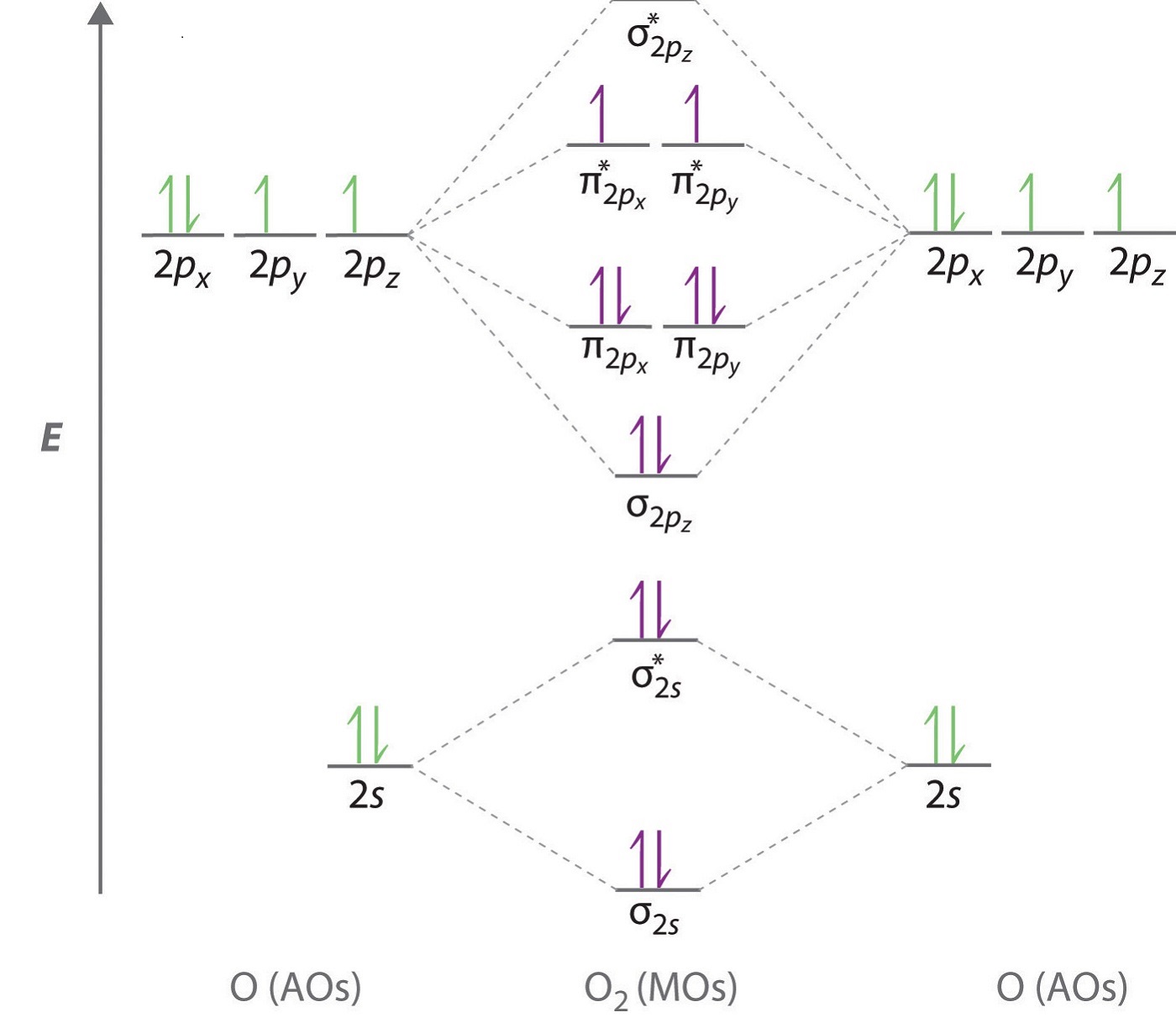
In the ground state of an atom, the orbitals are filled with electrons based on increasing order of energies of orbitals, Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity.
Order of atomic orbitals full#
This is because of extra stability of half- filled and full filled orbitals. Aufbau principle gives the sequence in which various orbitals are filled with electrons. However, some elements like chromium, copper, rhodium, silver and ruthenium do not follow the Aufbau principle. Electron configuration The arrangement of electrons in. If the added electron goes into a bonding orbital, the bond order would increase, making the. Electron orbitals the different energy levels filled by electrons within an atom (s, p, d, and f). The order of the energy of orbitals can be found out with the help of the $\left(. Geometry Hybridization Unhybridized p atomic orbitals. the lowest energy orbitals will be filled first. In other words, the orbitals having higher energies are filled only after the orbitals with lower energies are completely filled. Aufbau principle explained the sequence in which electrons occupy the orbitals, i.e. Electrons can not just exist at any distance from the nucleus. It says that the electrons occupy those orbitals first whose energy is the lowest. Electrons exist around the nucleus of an atom in discrete, specific orbits. This energy level diagram differs from the. We can understand the Aufbau principle in few points as: The hydrogen-like orbitals for a many-electron atom are listed in order of increasing energy in Fig. According to the principle, in the ground state of any atom or ion, the electrons fill the atomic orbitals in increasing order of their energies, that is, filling the lower available energy levels first before the higher levels. This gives the following order for filling the orbitals: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p, (8s, 5 g, 6f, 7d, 8p, and. The Aufbau principle depicts the order in which electrons are filled in the orbitals of an atom in its ground state. The Schrodinger equation dictates the energy order of the orbitals: (but they can be readily determined by looking at the periodic table or using a simple. Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the Aufbau principle.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
